Baseline Assessment
Vincent Astor Distinguished Professor of Medicine
Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Weill Cornell Medical College in NYC
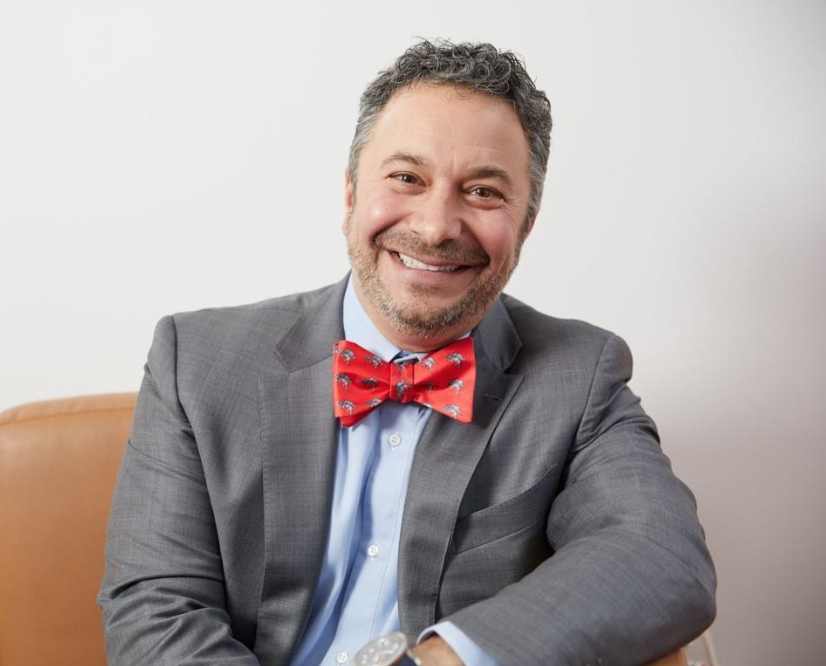 Robert S. Brown, Jr., MD, MPH is the Vincent Astor Distinguished Professor of Medicine and Chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City. He is also the co-founder and director of the Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation at New York-Presbyterian Hospital. He received his AB from Harvard College, his MD from New York University, and an MPH from the University of California, Berkeley. He did his residency at Beth Israel Hospital/Harvard Medical School and a fellowship in gastroenterology and hepatology at UCSF. He has co-authored over 250 peer-reviewed articles, an H-index of 102, and is the Editor-In-Chief for Liver Transplantation.
Robert S. Brown, Jr., MD, MPH is the Vincent Astor Distinguished Professor of Medicine and Chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York City. He is also the co-founder and director of the Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation at New York-Presbyterian Hospital. He received his AB from Harvard College, his MD from New York University, and an MPH from the University of California, Berkeley. He did his residency at Beth Israel Hospital/Harvard Medical School and a fellowship in gastroenterology and hepatology at UCSF. He has co-authored over 250 peer-reviewed articles, an H-index of 102, and is the Editor-In-Chief for Liver Transplantation.
Associate Professor of Medicine
Service Chief, Adult Allergy and Immunology
Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children's Hospital
Division of Immunology, Allergy & Retrovirology
 Dr. Joud Hajjar is an Associate Professor of Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and Service Chief of Adult Allergy & Immunology at Texas Children’s Hospital. She is a clinical immunologist specializing in inborn errors of immunity, antibody deficiencies, and immune dysregulation. Dr. Hajjar leads translational research on the microbiome and diagnostic assays and serves in national leadership roles with the Clinical Immunology Society, including as an elected councilor and as chair of the Adult Immunodeficiency Committee and the Women in Clinical Immunology Committee.
Dr. Joud Hajjar is an Associate Professor of Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and Service Chief of Adult Allergy & Immunology at Texas Children’s Hospital. She is a clinical immunologist specializing in inborn errors of immunity, antibody deficiencies, and immune dysregulation. Dr. Hajjar leads translational research on the microbiome and diagnostic assays and serves in national leadership roles with the Clinical Immunology Society, including as an elected councilor and as chair of the Adult Immunodeficiency Committee and the Women in Clinical Immunology Committee.